Delta Divergence in Options Trading
Options trading offers a world of possibilities for investors aiming to diversify portfolios and enhance returns. Yet, many traders struggle to identify optimal entry and exit points, often overwhelmed by market complexities. Enter Delta Divergence in Options Trading—a powerful concept that helps traders analyze option price movement relative to underlying assets. By leveraging delta divergence, traders can fine-tune their strategies to exploit inefficiencies and maximize returns.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essence of delta divergence, how it works, and actionable steps to incorporate it into your trading strategy. Whether you’re a options trader or a seasoned investor, understanding delta divergence can unlock new opportunities and sharpen your trading edge.
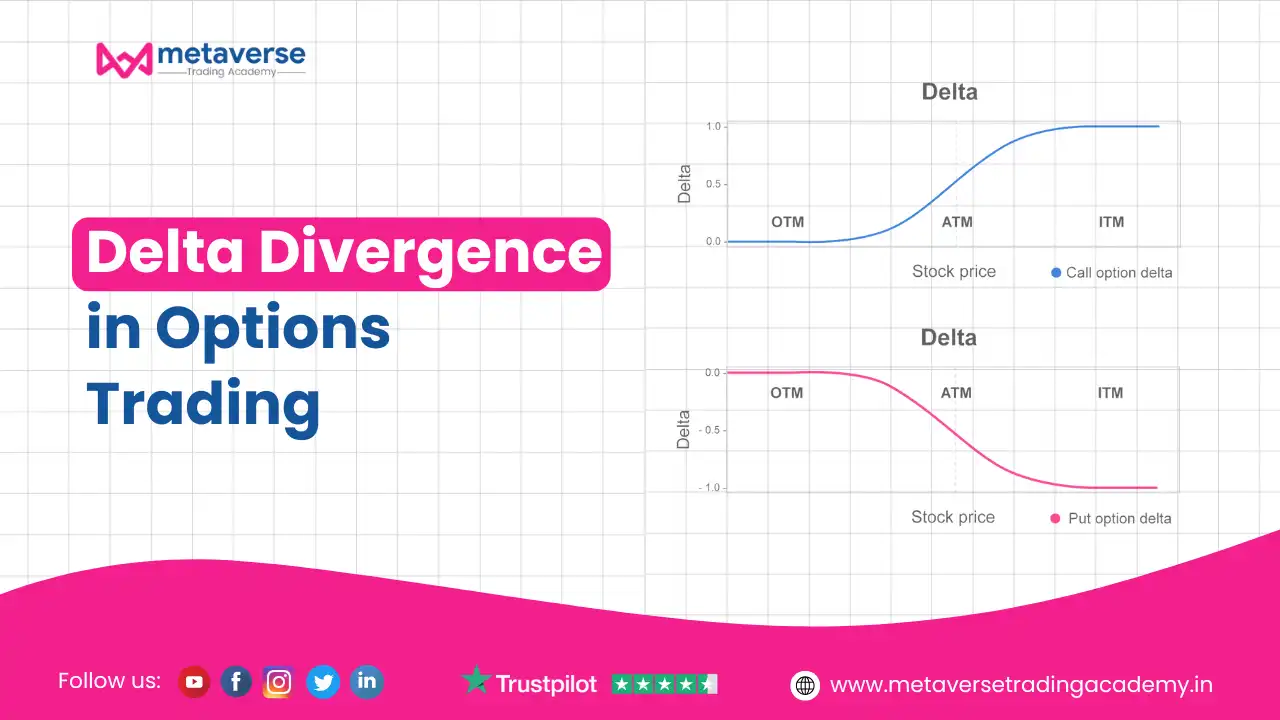
Delta in options trading is a crucial metric that measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the price of its underlying asset. It quantifies how much the premium of an option is expected to change for every $1 move in the underlying asset. Represented as a value between -1 and 1, delta serves as a guide for understanding an option’s directional exposure and potential profitability. For call options, delta values range from 0 to 1, indicating a positive relationship where the option’s price increases as the underlying asset rises. Conversely, put options have delta values ranging from -1 to 0, reflecting a negative relationship where the option’s price declines as the asset rises.
Delta also indicates the probability of an option expiring in-the-money; for instance, a call option with a delta of 0.7 suggests a 70% likelihood of finishing in-the-money. Beyond directional bias, delta is a valuable tool for hedging and risk management. It helps traders create delta-neutral strategies by balancing positions to minimize exposure to price fluctuations in the underlying asset. However, delta is dynamic and influenced by several factors, including changes in the asset’s price (gamma), time decay (theta), and shifts in implied volatility (vega). This evolving nature makes delta an essential consideration for adjusting positions over time. By mastering delta, traders can make informed decisions about position sizing, entry and exit strategies, and portfolio adjustments, optimizing their trading outcomes in the ever-changing markets..
For example:
Delta values range from -1 to 1:
Delta divergence occurs when there is a mismatch between the expected delta movement of an option and the actual price behavior of the underlying asset. This phenomenon can reveal discrepancies, often caused by changing market conditions, implied volatility shifts, or mispriced options.
Why is delta divergence important?
Imagine trading a call option with a delta of 0.7, expecting its price to rise significantly as the stock climbs. However, the option’s price remains stagnant due to high implied volatility or low liquidity. Understanding delta divergence in such scenarios can help you pivot strategies effectively.
Delta divergence in options trading refers to the difference in the delta of two options, usually within the same underlying asset or market. Delta itself measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in the price of the underlying asset. A delta of 0.5, for example, indicates that for every $1 movement in the underlying asset, the option’s price is expected to change by $0.50.
Traders use delta divergence to spot opportunities or risks by comparing the delta values of different options—typically calls and puts—for the same underlying stock. The goal is to identify when the delta of options diverges unusually from what is expected based on the underlying asset’s price movement. For example, if the stock price moves significantly but the delta of the corresponding call option doesn’t change as anticipated, this could signal that the option is underpriced or the market is mispricing volatility.
One practical application of delta divergence is in creating hedging strategies. For instance, if an option’s delta does not align with the price movement of the underlying asset, a trader might use this information to adjust their portfolio or open positions to reduce exposure to risk. Traders may also use delta divergence to spot arbitrage opportunities, especially in scenarios where mispricing occurs between different expiration dates or strike prices.
Overall, delta divergence provides valuable insight into how market conditions, volatility, and pricing inefficiencies may affect options positions. By analyzing delta divergence, traders can make more informed decisions regarding risk management, trade execution, and potential profit opportunities, especially in volatile or uncertain markets.
Delta divergence arises from several factors:
By identifying these causes, traders can better interpret divergence and make data-driven decisions.
To detect delta divergence:
Pro Tip: Tools like Thinkorswim or TradingView provide customizable delta metrics to help visualize divergence in real-time.
Once you spot delta divergence, consider these actionable strategies:
While delta divergence presents opportunities, it also involves risks. Follow these tips to minimize potential downsides:
For enhanced accuracy, integrate delta divergence with complementary tools:
Avoid these pitfalls to maximize the effectiveness of delta divergence:
Pro Tip: Regularly backtest your delta divergence strategy to refine its reliability in different market conditions.
Delta divergence is a game-changer for options traders seeking maximum returns. By understanding how delta interacts with the underlying asset and identifying divergence patterns, you can uncover lucrative opportunities while mitigating risks.
The key to success lies in blending delta divergence with robust risk management practices and complementary indicators. Continuously monitor market conditions and refine your approach to stay ahead of the curve.
Start exploring delta divergence in options trading today to unlock its full potential. Dive deeper into advanced trading strategies and sharpen your skills with our expert resources.
Ready to take your options trading to the next level? Check out our comprehensive options trading mentorship now!